2. Communication
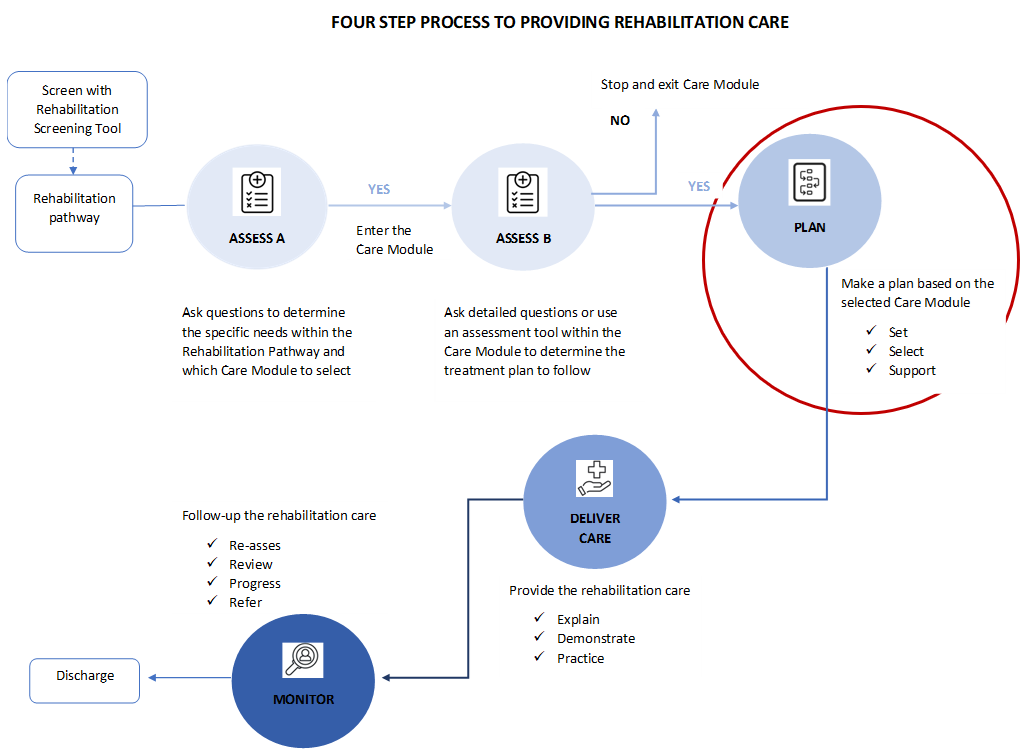
Planning for motor function and mobility rehabilitation interventions involves:
- Setting a goal
- Selection of rehabilitation interventions
- Supporting where needed with assistive technology
For more information on rehabilitation goal setting, see the introduction to rehabilitation module.

1. Setting a goal which is
- Functional
- Specific
- Time-bound
- Achievable
- Relates to everyday activities.
If people require rehabilitation across multiple care pmodules, it may be necessary to set a goal for each of the care module.
It is important to discuss goals with the person, and their family if appropriate.
![]() Activity
Activity

Remember David?
David finds it difficult to get up out of his bed or chair because of muscle weakness and stiffness in his joints.
Once he is standing, he uses a walking frame to walk short distances in his home.
Leitangi also assists him as needed.
Work in pairs, one person is David, and the other is the health worker.
Together, discuss and agree on a suitable goal for David.
Post and discuss your goal on the discussion forum.2. Selection of rehabilitation interventions
Rehabilitation interventions selected for each person depends on:
- The results of the assessments
- The goals, preferences and personal situation of the person.
Rehabilitation interventions may include:
- Non-pharmacological - Promotive, Preventive, Restorative and/or Compensatory interventionsProvision of assistive products
- Pharmacological agents.
Some people will benefit from a combination of interventions.
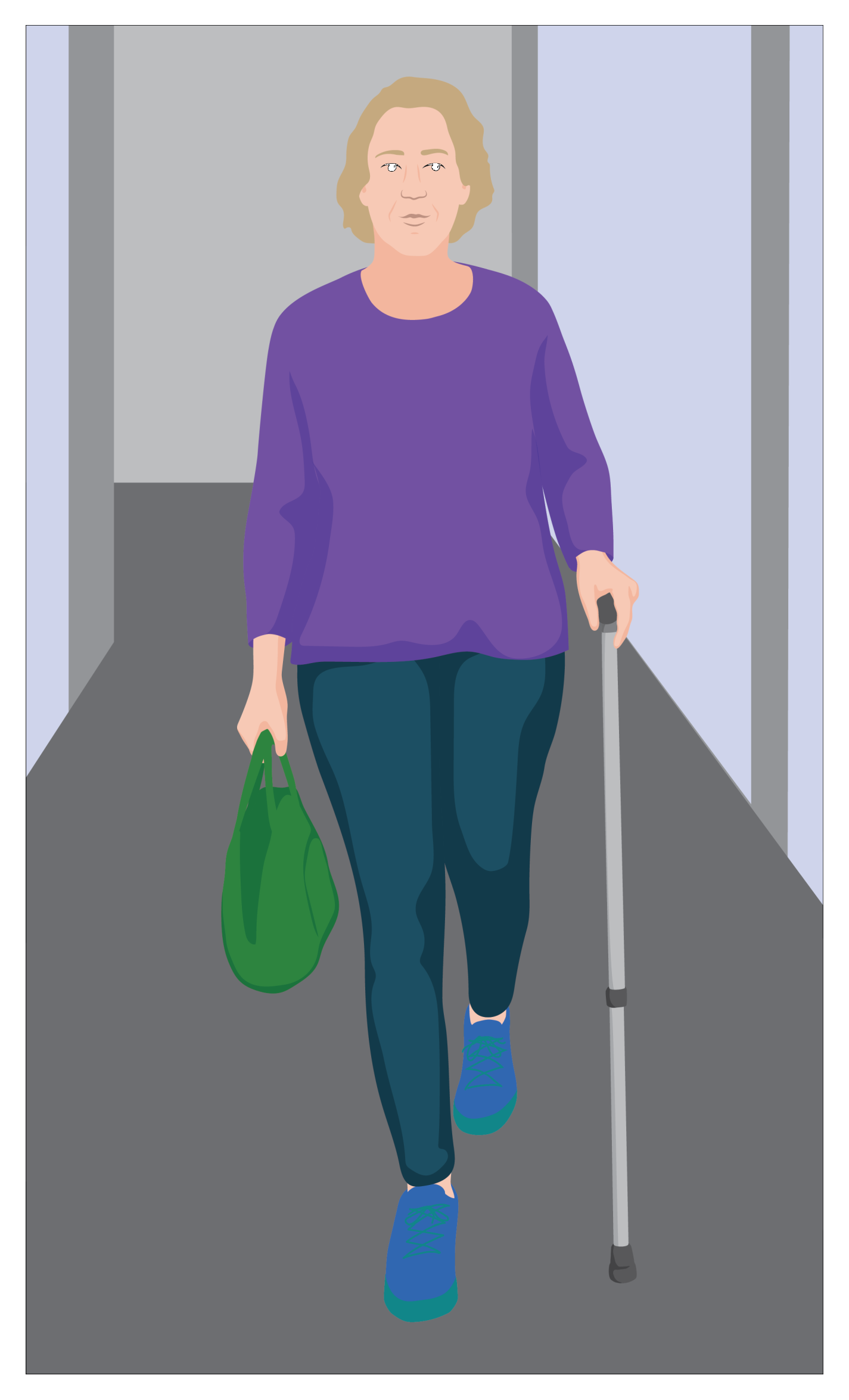

Kate had an accident and was hit by a car six months ago. Kate is able to walk by herself at home, and complete her everyday activities.
Kate uses a walking stick for longer distances outside.
Kate’s rehabilitation care included:
- Stretching to maintain range of motion of muscles and joints
- Muscle strengthening exercises to restore function
- Assistive products for self care activities at home
- Wheelchair provision when she discharged from hospital
- A walking stick to make it easier and safer for her to walk outside
- Analgesics for pain management.
Refer to the relevant TAP module for how to provide mobility assistive products
