2. Step One – Assess
The first step in providing rehabilitation is to assess the patient, this occurs within the Rehabilitation Pathway and within the Care Module.
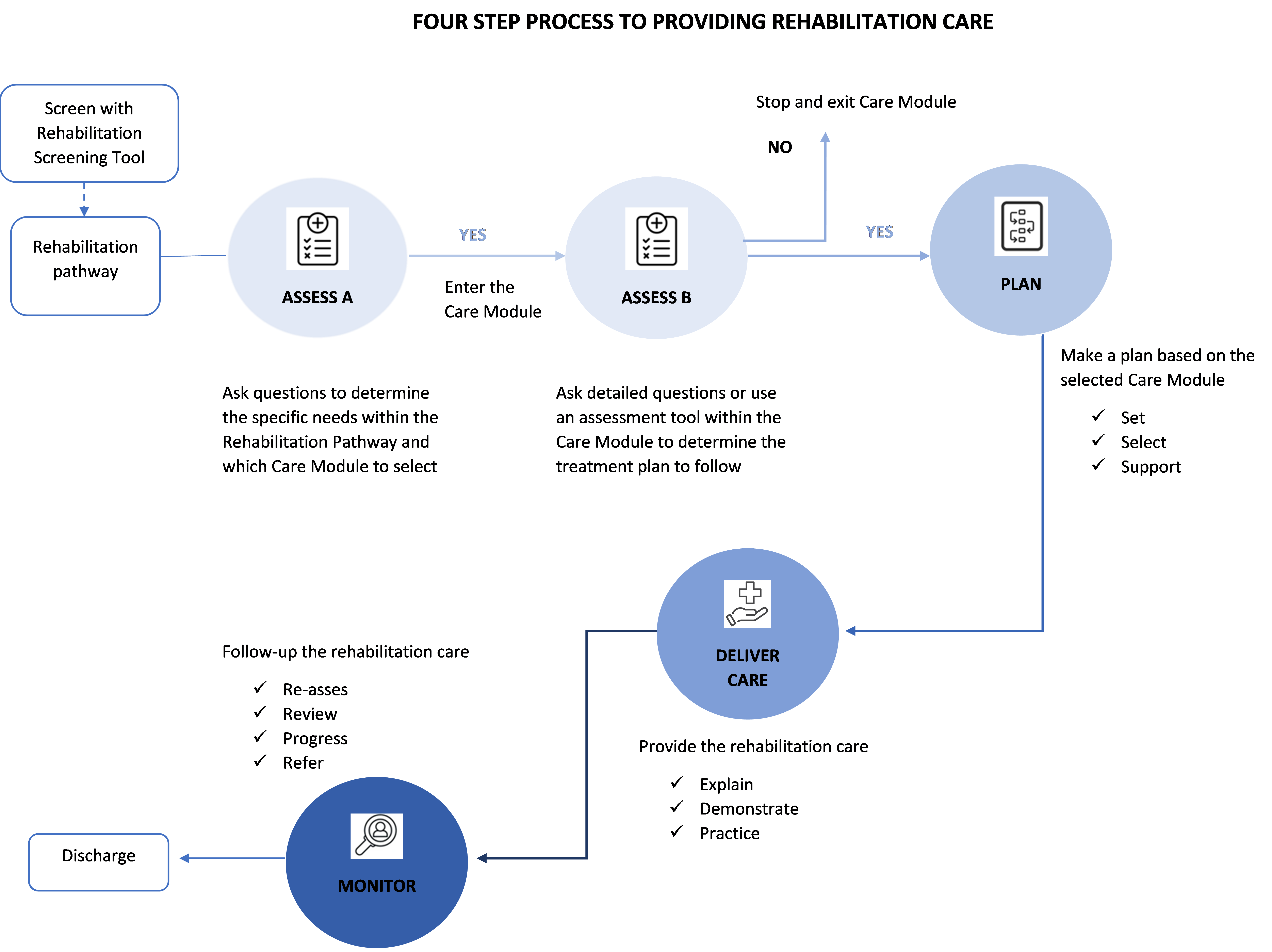
Assessment is conducted in 2 steps:
a. Assess A: Assess for areas of difficulty within a rehabilitation pathway.
This will enable the identification of the area of difficulty a patient experiences and indicate which Care Module is then required. It usually involves asking questions and observations.
For example, a person, who following screening is found to have difficulty in the Motor functions and Mobility pathway will be asked if there is a difficulty with Walking, transfers, or a feeling of muscle weakness. There is also a prompt to observe the way they walk as they enter the clinic / care setting. A person screened into the Self-care functioning domain will also be asked in this initial step if there is difficulty with bathing and dressing, feeding, doing household chores etc.
If there is a ‘NO’ answer to a specific question and difficulties are not observed, then there is no need to move to the next step and other questions in the rehabilitation pathway can be asked. There are multiple questions in this first step of the clinical decision tree and it is important to ask all the questions in order to know all the areas of difficulties the person experiences.
If there is a 'YES' answer to any of the initial questions, move to next stage of assessment.
b. Assess B: Assess for areas of difficulty within a Care Module
Assess B occurs within the Care Module, it involves: further questions or observations, as well as assessment tasks or tests such as assessing someone’s muscle strength or their joint range of movement.
Assessment B is the assessment that determines the specific rehabilitation intervention that should be provided. For example, if a person answered ‘YES’ to feelings of muscle weakness in the Rehabilitation Pathway for Motor functions and mobility, the next step is to enter the Care Module for muscle strengthening and identify where the muscles weakness is experienced and assess the extent of muscle weakness in the muscle as this then informs the specific rehabilitation intervention (muscle strengthening exercise) to be provided.
![]() Question
Question
Remember Kofi?
Initial screening questions for Kofi indicated he had difficulties in the following two rehabilitation pathways:
- Motor functions and mobility rehabilitation pathway
- Activities of Daily living, Bowel and Bladder, Community and Social life (Self-care) rehabilitation pathway
This means Assessment A is now required for both of these Rehabilitation Pathways. This is done by assessing for Kofi’s areas of difficulty within the rehabilitation pathways.
Kofi is asked ALL the questions in the self-care rehabilitation pathway and the motor functions and mobility rehabilitation pathway using their respective clinical decision trees. Kofi is also carefully observed. This assessment (Assessment A) reveals that
Kofi has weak muscles, cannot move from sitting to standing without support, walks only a short distance, does not have full control of his bladder and no longer can do his farming. This indicates that further assessment (Assessment B) is required.
Following your assessment and findings, which of the Care Modules do you think Kofi requires?
- Muscle strengthening – Kofi has weak muscles
- Gait/Walking – Kofi is unable to walk
- Transfers – Kofi cannot move from sitting to standing without support
- Bowel and bladder – Kofi cannot fully control his bladder
- Community and social engagements – Kofi can no longer go to the farm
Following the instructions in the Care Modules it is now necessary to (with Kofi’s full participation)
- Further assess Kofi’s muscle strength, gait, ability to transfer, self-care and identify his rehabilitation care
- Draw a plan for managing Kofi’s self-care as well as his motor functions and mobility.
