2. What are rehabilitation interventions
Rehabilitation interventions are health interventions that aim to achieve and maintain optimal levels of functioning in people with health conditions, considering their environmental and personal situation. They can be grouped under two (2) categories:
1. Non-pharmacologic interventions
These include:
Promotive, Preventive, Restorative and Compensatory (PPRC) interventions – PPRC interventions are interventions that target all functioning domains (body functions, structures, activities and participation and personal factors) and that aim to;
a. prevent barriers to functioning
b. promote or maintain functioning
c. specific aspects of functioning, or,
d. compensate for aspects of functioning that cannot be restored.
They may take the form of educating, advising or counselling on health conditions and ways to prevent or manage them, training on how to perform exercises, providing supplements or administering products directly.
a. Provision of Assistive Products – An assistive product is any external product (including devices, equipment, instruments or software), especially produced or generally available, the primary purpose of which is to maintain or improve an individual’s functioning and independence, and thereby promote their well-being. Assistive products are also used to prevent impairments and secondary health conditions. They support a person to be included and participate in what that they want or need to do. In order to improve a person’s functioning such as mobility, self-care, hearing and cognition, an assistive product is provided as part of rehabilitation.
2. Pharmacologic interventions
Pharmacological agents used in rehabilitation include analgesics, antispastic medications, bronchodialators and antidepressant medications.
![]() Question
Question
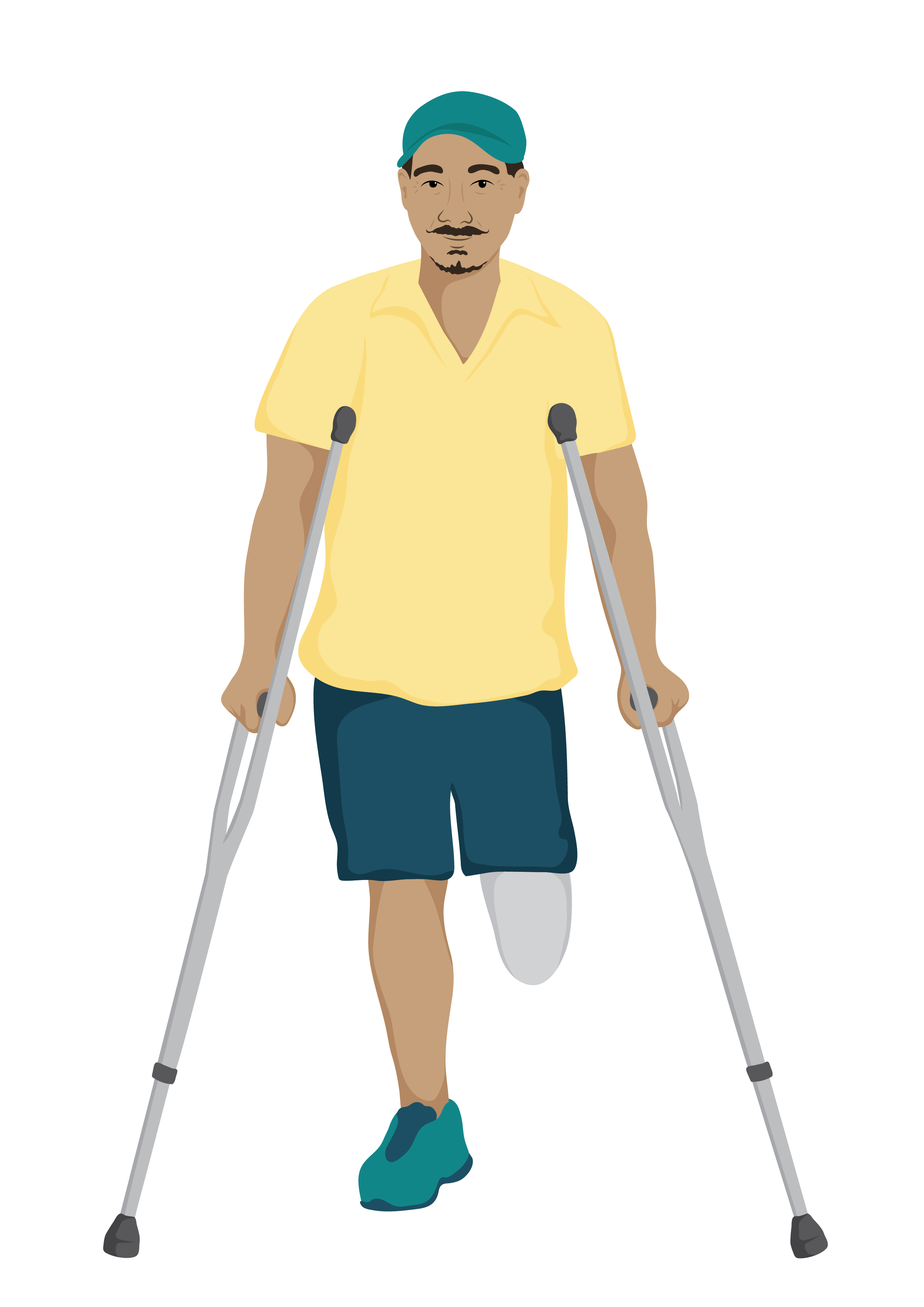
Meet Dai
Dai is 65 years old and was recently involved in a road traffic accident. He had a right below knee amputation as well as damage to his pelvis.
During an assessment interview at the local clinic, Dai tells you that he can get into the family bathroom at home. However, they have a squat toilet, and he cannot squat.
He also experiences pain when standing, and finds standing to wash himself very difficult. Dai is feeling sad because he thinks he can no longer work as a result of his amputation.
On examination, you noticed that Dai has stiffness in his left hip joint.
You educated and counselled Dai on amputation, the options available for work and the social support systems available including a local amputee support group. Together with Dai, you made the following plan;
1. To get Dai axillary crutches while planning for a prosthetic leg.
2. To teach Dai range of motion exercises in his hip in order to improve his hip movement.
3. To educate Dai on how to care for the skin of his leg stump to prevent pressure wounds.
4. To prescribe for Dai pain medications and anti spastic medications
Outline how
the categories of rehabilitation interventions have been represented in Dai’s
story.
1. Non-pharmacologic (PPRC interventions/Provision of assistive products)
Preventive: Education on skin care
Promotive: Education and counselling on work and social support options
Restorative: Range of motion exercises
Compensatory: Prosthetic leg
Provision of assistive products: Axillary crutches / Prosthetic leg
2. Pharmacologic
Provision of pharmacological agents: pain medications, anti spastic medications
