5. What health conditions commonly benefit from rehabilitation for motor function and mobility?
Read on to find out more about common health conditions that could benefit from motor function, mobility and pain rehabilitation.
Stroke
A person with a stroke may benefit from preventative, restorative or compensatory interventions related to motor function and mobility, focused on:
- Improving muscle strength and endurance
- Improving coordination (gross and fine motor)
- Maintaining range of motion of muscles and joints
- Improving balance
- Improving communication (verbal and non-verbal)
- Ensuring safe swallow of food and water
- Managing bowel and bladder continence
- Managing every day activities such as household chores
- The use of assistive products such as walking aids, continence products, modified eating and drinking aids, and orthoses.
Pharmacological interventions may also be successful, including:
- Analgesics: for pain management
- Antispastic / antispasmodic: To relax contracted or overactive muscles.
![]() Question
Question
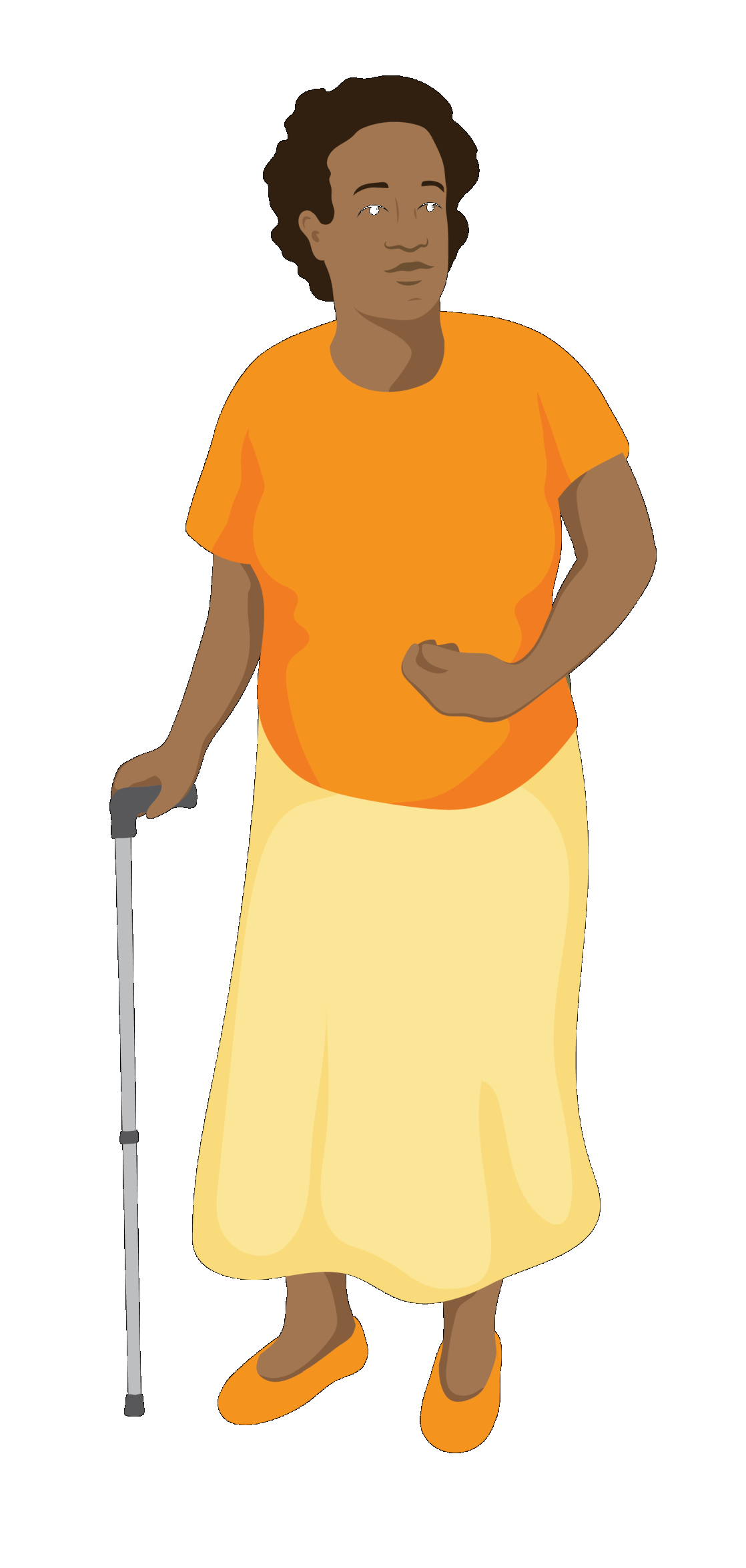

Meet Aida
Aida is 53 and lives close to her daughter. Aida has had a stroke. This has caused weakness on the left side of her body.
Aida finds it hard to balance while standing and walking, and using her left arm for everyday activities, such as getting dressed or undressed.
Her health worker has provided:
- Exercises to maintain strength in her right leg (non-affected side) and build strength in her left leg (affected side)
- Exercises and stretches to maintain range of motion in her upper limb (arm and hand).
- A walking stick to help with her mobility.
Aida’s daughter sometimes assists her with her everyday activities including getting dressed in the morning.
Which of the following are examples of a compensatory intervention?
Select all that apply.
- a. Providing stretching exercises to maintain range of motion in the upper limb
- b. Providing a walking aid to support mobility
-
c. Providing exercises that strengthen the non-affected side of the body.
If you selected b, you are correct. A walking aid is an example of a compensating for a person with a mobility difficulty.
Frail / frailty
A person who is frail may benefit from promotive, preventive and compensatory interventions, focused on:
- Maintaining muscle strength and endurance
- Maintaining range of motion of muscles and joints
- Maintaining balance
- Improving ability to engage in self care activities such as bathing, dressing, continence
- Managing every day activities such as doing household chores
- The use of assistive products such as walking aids, continence products, toilet and shower chairs.
Meet David
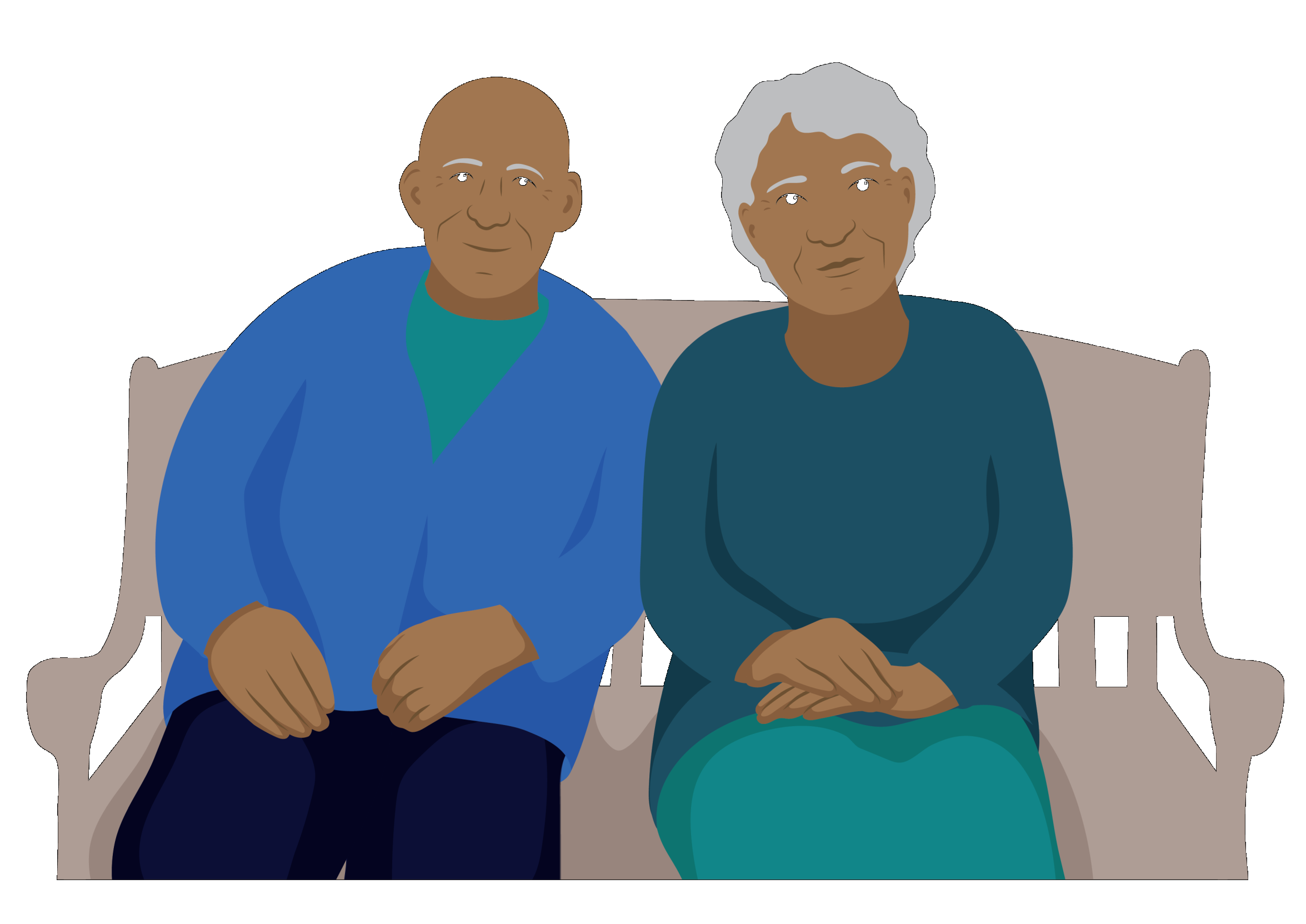

David is an older, frail man who lives with his wife, Leitangi.
He finds it difficult to get out of his bed or chair because of muscle weakness and stiffness in his joints.
David uses the arm rests to push up from the chair. Once he is standing, he uses a walking frame to walk short distances in his home. He has been taught by his health worker how to go about his daily activities as independently as possible.
He uses other assistive products to help him with his everyday activities. Leitangi also assists him as needed.
Amputation
People with lower limb amputations may benefit from preventative and compensatory interventions focused on:
- Improving muscle strength
- Improving coordination (gross and fine motor)
- Maintaining range of motion of muscles and joints
- Improving balance
- Managing self care activities such bathing or dressing
- Managing every day activities such as using transportation and household chores
- The use of assistive products such as walking aids, toilet and shower chairs and prostheses.
Pharmacological interventions may also be successful, including:
- Analgesics: for pain management post-surgery
Meet Ruhaan
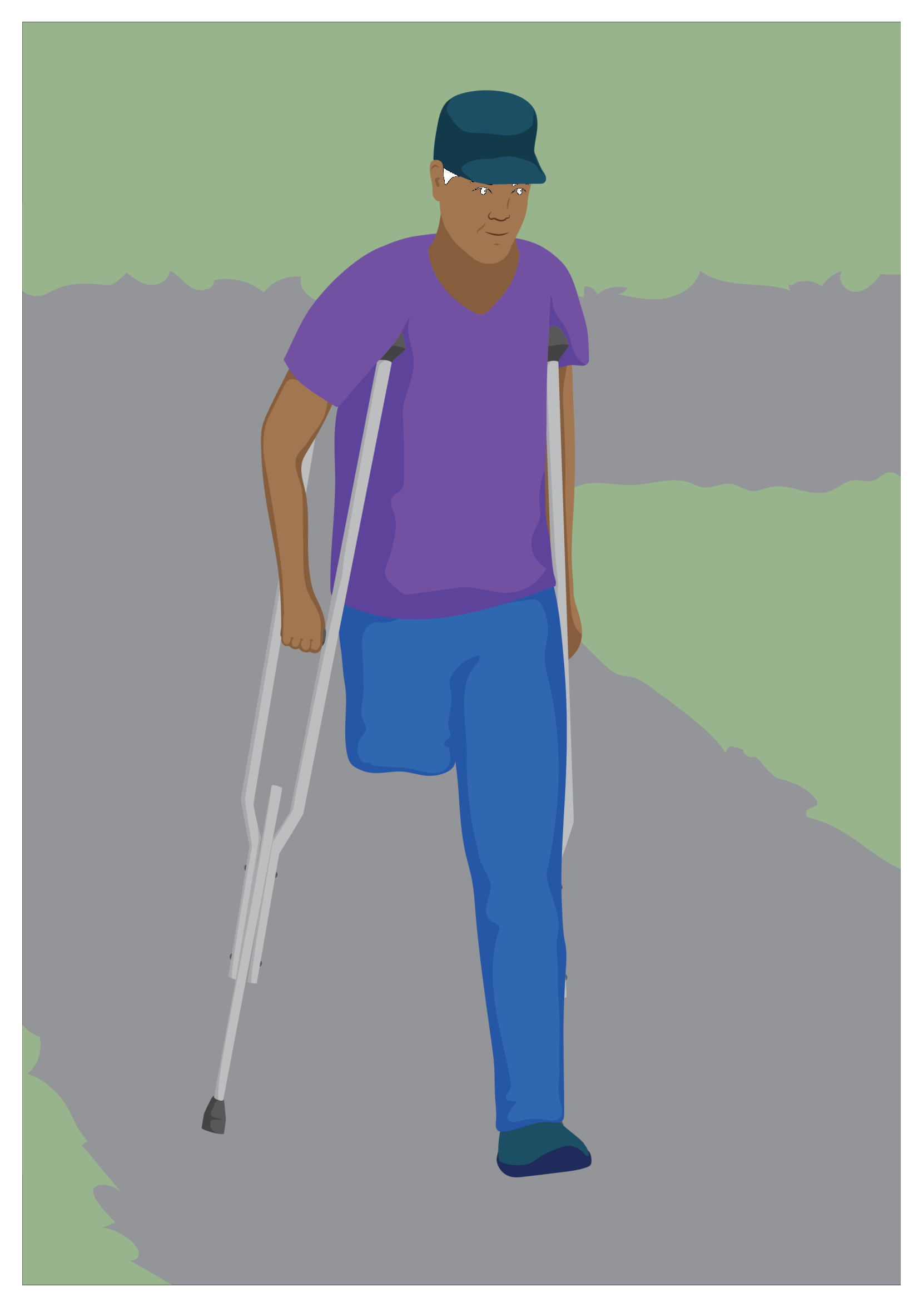
Ruhaan recently had a left transfemoral (above knee) amputation after an accident at work.
Ruhaan received rehabilitation services while an inpatient in hospital, including:
Muscle strength:
- Exercises to maintain muscle strength in his residual limb, ready for a prosthesis.
- Exercises to maintain muscle strength in his remaining limb.
Maintaining range of motion of his left hip:
- Advice on the best way to sit or lie down
- Stretches to prevent muscles and ligaments in his hip from developing contractures.
Provision of assistive products:
Ruhann was provided with walking aids for mobility, and a shower chair to sit on while showering and getting dressed.
Ruhann has been referred for a prosthesis, and is looking forward to his first appointment.
Trauma-related injuries
Trauma-related injuries often occur from road traffic accidents, falling from a height, crush injuries from a collapsing weight or physical assault.
Multi-trauma injuries may require many weeks or months of hospital care.
A person who has trauma-related injuries may benefit from preventative, restorative and compensatory interventions, depending on their injury. Interventions may focus on:
- Improving muscle strength and endurance
- Improving coordination (gross and fine motor)
- Maintaining range of motion of muscles and joints
- Improving balance
- Managing self-care activities such as bathing, dressing
- Managing every day activities such as using transportation, doing household chores.
Pharmacological interventions may also be successful, including:
- Analgesics: for pain management
![]() Question
Question
Which of
the following injuries or complications from trauma may benefit from motor
function and mobility rehabilitation?
Correct
A fracture of the leg can result in difficulty walking. The person may benefit from learning how to mobilise safely with a walking aid or wheelchair.
Correct
A person with an amputation of the leg results in difficulty walking. The person may benefit from muscle strengthening and range of motion exercises.
Correct
A traumatic brain injury can result in problems with balance, coordination and muscle strength which would benefit from muscle strengthening exercises.
Diabetes
A person with diabetes may benefit from promotive, preventative, restorative or compensatory interventions, focused on:
- Improving muscle strength and endurance
- Improving fine motor skills (when sensation is affected)
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Managing self-care activities such as cooking to prevent burns as a result of reduced feeling (sensation)
- Preventing foot wounds with appropriate footwear and daily foot checks.
Pharmacological interventions specific to diabetes management should also be considered.
![]() Question
Question
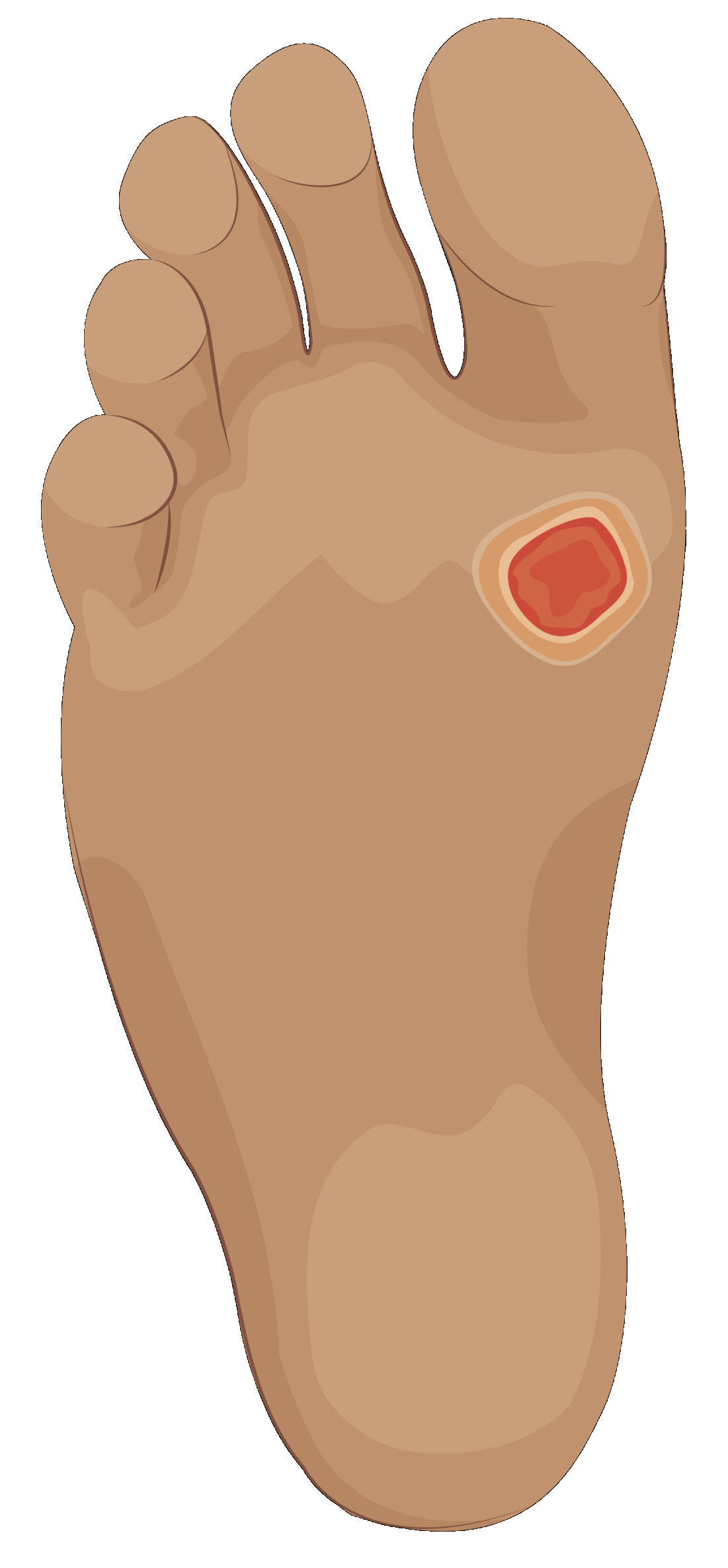
Common complications for many people with diabetes are untreated foot wounds that become infected and require intensive treatment, surgical debridement or amputation.
For a person with a diabetic foot wound, you should encourage them to exercise by going for a light walk each day.
Select all that apply.
- a. True
- b. False
If you selected b, you are correct. Continuing to walk on a foot wound can cause further damage.
If a foot wound is not treated properly, it may result in infection, loss of mobility and amputation.
Health care workers can relieve pressure and prevent damage to the wound by:
- Providing mobility devices, such as walking aids or wheelchairs to support the person to be non-weight bearing while the foot wound heals
- Providing an offloading device, such as a total contact cast, that allows people to keep walk while the wound heals.
People
with diabetic foot wounds should be referred to a diabetic foot clinic or other
specialised medical service.
For more information about offloading for diabetic foot wounds, see the following TAP modules:
- Offloading
- Total contact casts
Osteoarthritis
A person with osteoarthritis may benefit from preventative, restorative, compensatory and focused on:
- Improving coordination (especially fine motor)
- Maintaining range of motion of muscles and joints
- Improving balance
- Managing self-care activities such as bathing, dressing,
- Managing every day activities such as using transportation, household chores, community and social activities.
Pharmacological interventions may also be successful, including:
- Analgesics: for pain management
- Anti-inflammatory: for pain and inflammation management.
Falls are common for people with osteoarthritis.
You will learn more about preventing falls during assessment or treatment session in lesson X.
Cerebral palsy
A person with cerebral palsy may benefit from preventative, restorative or compensatory interventions, focused on:
- Improving muscle strength and range of motion
- Improving coordination (gross and fine motor)
- Maintaining range of motion of muscles and joints
- Improving balance
- Coordinating speech and improving communication
- Improving ability to safely swallow food and drink
- Managing continence
- Ability to engage in social and community activities.
![]() Question
Question
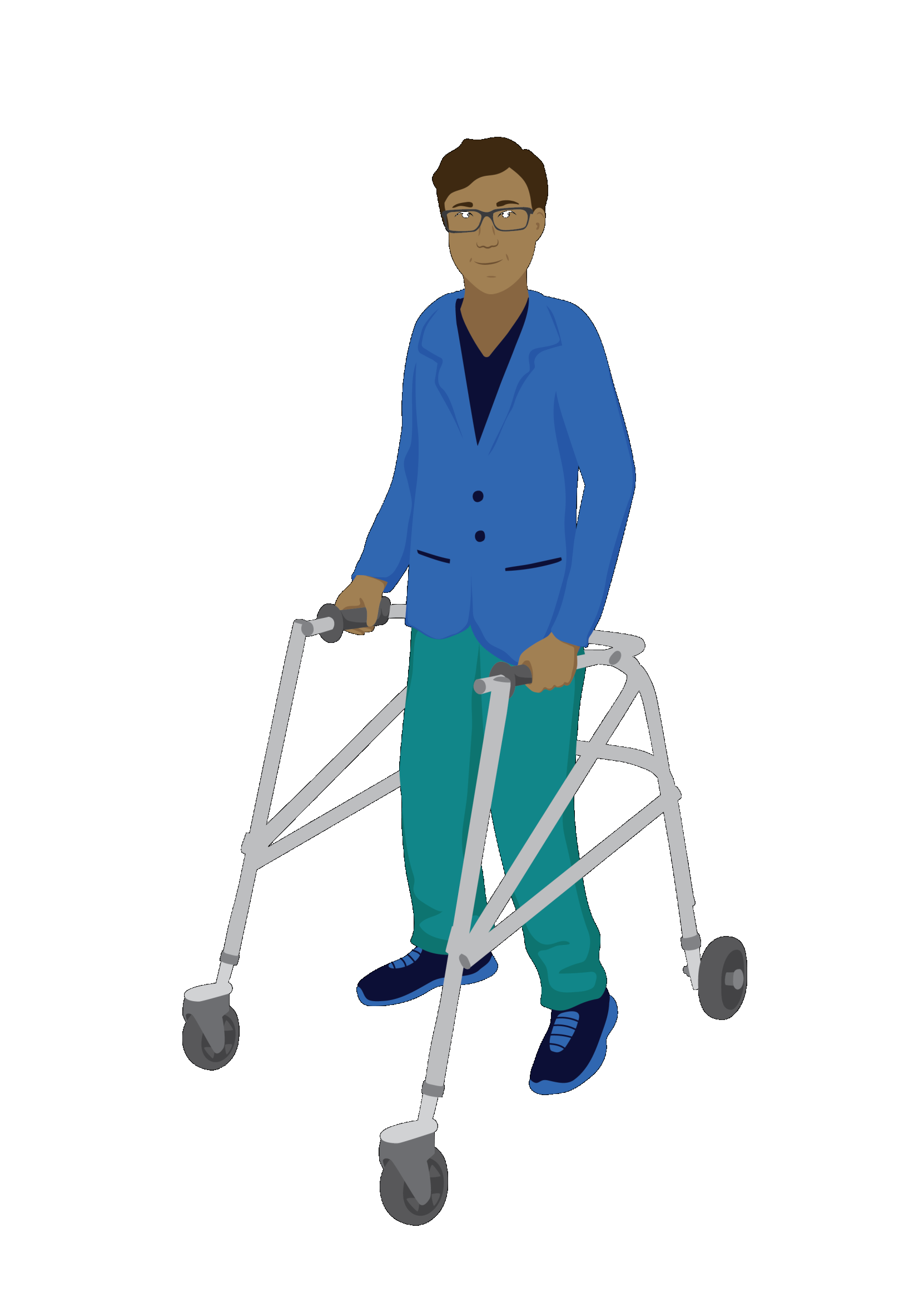
Meet Levi
Levi is a journalist. He was diagnosed with Cerebral Palsy at birth. He lives by himself, close to his workplace and family. He travels to and from work using public transport. Levi walks with a posterior walker. Sometimes he uses a wheelchair for long distance mobility.
Levi has a regular muscle strengthening and stretching programme that he completes, at home three times a week.
This helps to maintain Levi’s motor functions and mobility. His health care professional updates his programme once a year.
Levi’s muscle strengthening programme is an example of a promotive intervention.
Select all that apply.
- a. True
- b. False
If you selected b, you are correct.
Levi’s muscle strengthening and stretching programme aims to prevent muscles from becoming weak, and muscles and ligaments from developing contractures. It is an example of a preventive intervention.
Levi’s posterior walker is an example of a compensatory intervention.
Select all that apply.
- a. True
- b. False
If you selected a, you are correct. Assistive products that compensate for mobility difficulties is an example of a compensatory intervention.
Ischaemic Heart Disease
A person with Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) will benefit from preventative, promotive and restorative health interventions focused on:
- Maintaining and restoring heart health with gentle exercise each day
- Maintaining muscle strength and endurance needed for mobility and ADLs
- Support with maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle
Pharmacological interventions specific to IHD should also be considered
People with ischaemic heart disease are at increased risk of a heart attack.
A person with signs of heart disease which worsen with normal physical activity may not be suitable for physical rehabilitation.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
A person with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD) will benefit from preventative, promotive and compensative health interventions focused on:
- Maintaining and airway and lung health with gentle exercise each day
- Maintaining respiratory muscle strength and endurance through breathing exercises
- Support with learning positioning and techniques to assist with airflow and respiratory muscle recruitment
Pharmacological interventions specific to COPD should also be considered.
People
with severe COPD may not be suitable for physical rehabilitation.
![]() Question
Question
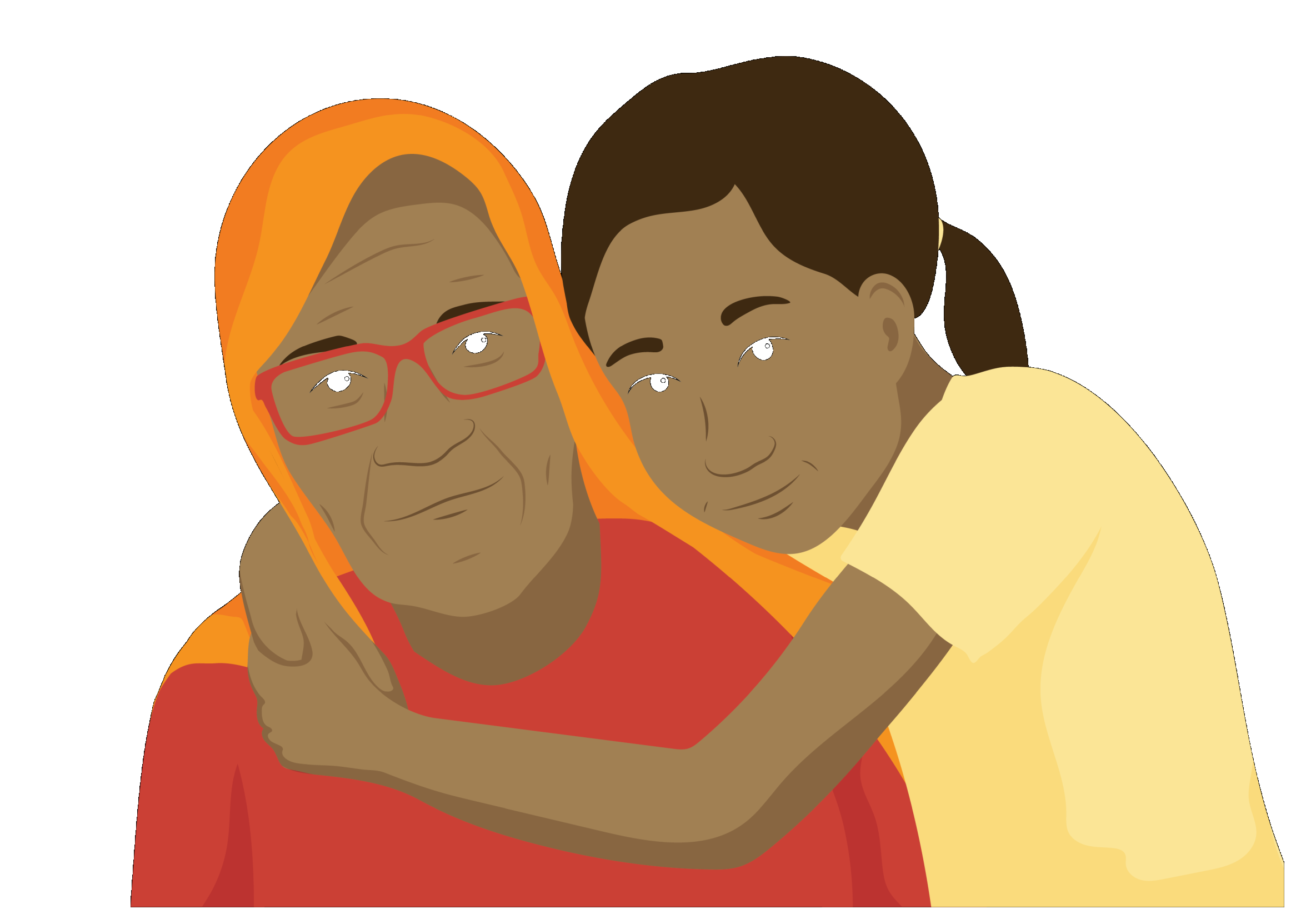

Meet Sai
Sarah is an older, frail woman. She lives at home with her husband, Aarav and her daughter’s family. Sai enjoys spending time with her granddaughter.
In the last two months, Sai has had several falls at home. Due to this, Sai went to her primary health care clinic, where you work, for assistance.
When you assess Sai, you find that she has developed muscle weakness and poor balance as part of the normal aging process. She does not use a walking aid but holds on to her husband, Aarav, when walking.
What rehabilitation interventions may assist Sai?
Select all that apply.
- a. Assessment to provide a walking aid to support her to balance while walking.
- b. Light exercise programme to maintain strength
- c. Exercises and stretches to maintain range of motion in her upper limb (arm and hand)
If you selected a and b, you are correct.
Assessing Sai for a walking aid that meets her needs, may assist her to walk more safely at home without the assistance of Aarav to walk.
A light exercise programme may help Sai to maintain her strength as she ages further.
You have completed Lesson one!
If you have any questions or comments, post them on the discussion forum.